Properties of White Gel Food Coloring: Gel Food Coloring White

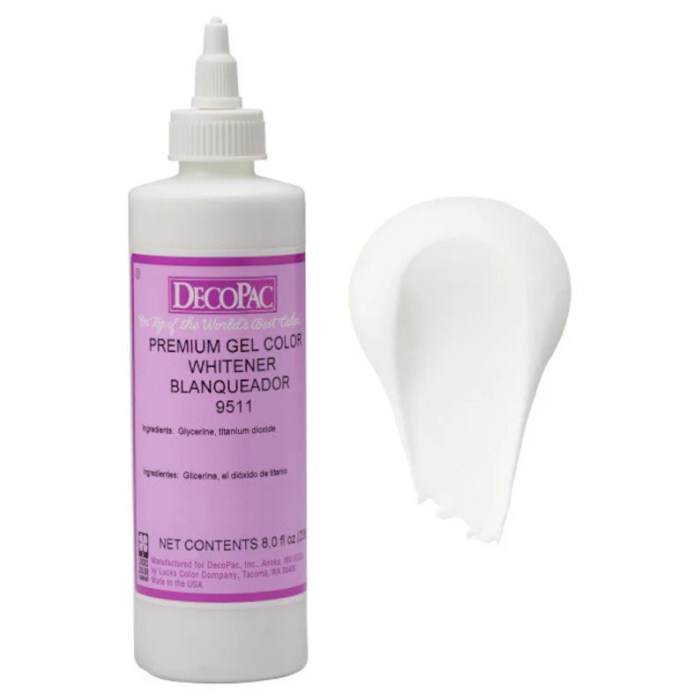
Gel food coloring white – White gel food coloring, while seemingly simple, possesses unique properties that distinguish it from other food coloring options. Understanding its composition and characteristics is crucial for both culinary applications and informed consumer choices. This section will delve into the specifics of white gel food coloring, clarifying its makeup and comparing it to its liquid counterpart.
Chemical Composition of White Gel Food Coloring
The chemical composition of white gel food coloring is primarily based on a blend of ingredients designed to create a thick, opaque white color and a stable texture. The base is typically a mixture of oils, often including mineral oil or vegetable oil, which provides the gel-like consistency. These oils act as a carrier for the other ingredients, allowing for easy dispersion and preventing the separation of components.
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is the key pigment responsible for the white color. This is a common food-grade additive known for its high opacity and reflective properties. Other ingredients may include stabilizers, emulsifiers, and preservatives to maintain the product’s quality and shelf life. The precise proportions of these ingredients vary depending on the manufacturer and specific product formulation.
Differences Between White Gel and Liquid Food Coloring
White gel food coloring differs significantly from its liquid counterpart in several key aspects. The most obvious difference is consistency: gel food coloring is significantly thicker and more viscous than liquid food coloring. This thicker consistency allows for more precise control and prevents excessive spreading or bleeding when used in decorating. Liquid food colorings, on the other hand, are more fluid and can be easily diluted with water or other liquids.
The higher concentration of pigment in gel food coloring generally results in a more intense color, requiring less to achieve the desired effect. Finally, gel food coloring often has a longer shelf life due to its thicker consistency and the inclusion of preservatives.
Gel food coloring white, a stark, almost unsettling blankness, offers a curious counterpoint to the vibrant hues of Easter. Its potential, however, extends beyond mere absence; consider its use as a base for pastel shades, or as a crucial ingredient when you’re learning the delicate art of coloring eggs with food coloring , where precise control is paramount.
Ultimately, the pristine white gel reveals itself as a potent tool, capable of both subtlety and surprising depth.
Typical Ingredients in Commercial White Gel Food Coloring
Commercial brands of white gel food coloring typically list the following ingredients on their labels: Titanium dioxide (TiO2) as the primary coloring agent, various oils (mineral oil or vegetable oils) as the base, glycerin or other humectants to retain moisture, and preservatives such as potassium sorbate to extend shelf life. Emulsifiers may also be included to ensure the stability of the mixture and prevent separation.
Specific brands may utilize proprietary blends of ingredients, but the core components generally remain consistent across various products. It’s always advisable to check the ingredient list of the specific brand being used to ensure compliance with dietary restrictions or preferences.
Consistency and Texture of White Gel Food Coloring
White gel food coloring possesses a unique consistency and texture compared to other food colorings. Unlike liquid food colorings, which have a watery consistency, white gel food coloring has a thick, paste-like texture, similar to a very thick cream or gel. This thick consistency is a key advantage, enabling precise application and control during decorating or coloring processes. Powdered food colorings, while also capable of producing intense colors, often require more thorough mixing and may create lumps if not properly incorporated.
The smooth, easily spreadable texture of gel food coloring makes it particularly well-suited for intricate designs and detailed work.
Uses in Food Preparation
White gel food coloring, despite its seemingly simple nature, offers a surprising versatility in culinary applications. Its concentrated pigment allows for precise color control, making it a valuable tool for bakers and decorators alike. Its neutral flavor ensures it won’t detract from the taste of your creations.
The uses of white gel food coloring extend beyond simply adding a touch of brightness. It acts as a crucial ingredient in achieving specific shades, textures, and visual effects in a wide range of desserts and confectionery items.
White Gel Food Coloring in Baking, Gel food coloring white
White gel food coloring can subtly enhance the appearance of baked goods. For instance, a small amount added to vanilla cake batter can brighten the color, making it appear more vibrant and appealing. In sugar cookies, it can create a crisp, clean white base perfect for intricate icing designs. Adding it to buttercream frosting allows for a smoother, more intense white color, avoiding the grainy texture sometimes associated with using powdered sugar alone.
Similarly, it can intensify the whiteness of meringue, creating a visually stunning contrast against other colored desserts.
Recipes Demonstrating the Use of White Gel Food Coloring
The following recipes illustrate how white gel food coloring can elevate the visual appeal of your creations:
Recipe 1: Bright White Vanilla Cupcakes: A standard vanilla cupcake recipe can be enhanced by adding a small amount (about 1/4 teaspoon per batch) of white gel food coloring to the batter. This intensifies the natural off-white color of the batter, creating a brighter, more visually appealing result. The addition of white gel food coloring doesn’t significantly impact the taste or texture of the cupcakes.
Recipe 2: Snow White Fondant: When making fondant, a small amount of white gel food coloring can create a brilliant white color that is free of any yellow or off-white undertones. This ensures the fondant is the perfect base for detailed decorations and sculpting. A standard fondant recipe can be adjusted by adding a few drops of white gel coloring until the desired shade is achieved.
White Gel Food Coloring in Fondant and Decorative Elements
White gel food coloring is indispensable for creating flawlessly white fondant. It allows for the achievement of a pure, bright white, free from any subtle yellowish tones often present in naturally white ingredients. This is especially crucial when creating delicate decorations or intricate designs where even slight color variations are noticeable. The gel’s concentrated pigment allows for precise control, ensuring a consistent, uniform color throughout the fondant.
It also works well with other colors, allowing for the creation of a wide range of shades by mixing it with other gel food colorings.
Creating Different Shades of White and Lightening Other Colors
White gel food coloring acts as a powerful tool for modifying color intensity. It can be used to create a spectrum of whites, from a bright, almost luminous white to a softer, more subdued off-white, simply by adjusting the amount added. Furthermore, it’s invaluable for lightening other colors. For instance, a small amount added to a pastel pink frosting can lighten the shade, creating a delicate blush pink, while a larger quantity will create a lighter, more washed-out effect.
Comparative Effects of White Gel Food Coloring in Different Foods
The following table compares the impact of white gel food coloring on various food types:
| Food Type | Effect on Texture | Effect on Taste | Effect on Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cake Batter | Minimal to no effect | No noticeable effect | Intensifies whiteness, brightens |
| Buttercream Frosting | May slightly increase smoothness | No noticeable effect | Creates a brighter, more intense white |
| Fondant | Minimal to no effect | No noticeable effect | Creates a pure, bright white |
| Cookies | Minimal to no effect | No noticeable effect | Creates a clean, crisp white |
Illustrative Examples

White gel food coloring, while seemingly simple, offers a surprising range of possibilities in culinary artistry. Its versatility allows for subtle enhancements or dramatic transformations depending on the application technique and desired effect. Let’s explore some specific examples to illustrate its potential.
A Delicately Decorated Cake
Imagine a three-tiered vanilla cake, each layer flawlessly smooth and ivory-white. This effect is achieved using a high-quality white gel food coloring incorporated into the batter itself, ensuring a consistent, deep color throughout. The frosting, a classic Swiss meringue buttercream, is also subtly tinted with a small amount of the gel coloring, creating a slightly off-white shade that complements the cake’s base color.
Delicate white lace patterns are piped onto the cake using a fine-tipped piping bag, showcasing the precise control and detail achievable with the coloring. The intensity of the white is even and bright, free from any chalky or grayish undertones, thanks to the high-quality gel. The texture of the buttercream, enhanced by the coloring, remains smooth and velvety, a testament to the coloring’s non-interference with the frosting’s consistency.
Creating a Marbled Cake Batter
To create a visually stunning marbled effect, we start with two separate bowls of vanilla cake batter. One bowl remains plain, while the other is delicately tinted with white gel food coloring to achieve a creamy white hue. The color is added gradually, ensuring even distribution to avoid streaks or clumps. Then, the white and plain batters are gently swirled together in a larger bowl, using a knife or spatula to create a beautiful, irregular pattern.
The resulting marble effect is not uniform; instead, it presents a captivating interplay of light and shadow, where streaks of white contrast beautifully with the natural color of the vanilla batter. This technique showcases the coloring’s ability to create a visual depth and complexity without significantly altering the texture of the cake.
Achieving a Specific Shade of White in Frosting
A recipe for a perfectly white buttercream frosting might start with a base of unsalted butter, powdered sugar, and a touch of milk or cream. The key to achieving a specific shade of white, however, lies in the precise addition of white gel food coloring. Instead of adding the coloring all at once, a small amount is incorporated initially, thoroughly mixed, and then more is added incrementally until the desired shade is reached.
For instance, to achieve a brilliant, almost luminous white, a slightly higher concentration of coloring might be used. For a softer, more creamy white, a lesser amount is sufficient. This controlled approach ensures a consistent, even color throughout the frosting, preventing any patchy or uneven areas. The final result is a smooth, flawlessly white frosting, ready to be used for decorating cakes, cupcakes, or other confections.
The texture remains smooth and creamy, proving the gel’s ability to enhance visual appeal without compromising texture.
FAQ Summary
Can I use white gel food coloring in savory dishes?
While primarily used in sweets, it can subtly brighten the appearance of some savory dishes, but its impact might be minimal. Taste and texture are unlikely to be affected.
Does white gel food coloring have a taste?
High-quality white gel food coloring is generally flavorless. However, using excessive amounts might slightly alter the taste of your recipe.
How much white gel food coloring should I use?
Start with a small amount and gradually add more until you achieve your desired shade. It’s always better to add less and build up the color than to add too much.
Can white gel food coloring be used with other food colorings?
Yes, it can be used to lighten other colors or create custom shades. Experiment to find the perfect combination.